(알고리즘) 피보나치 (재귀와 분할정복)
기존 피보나치의 수열을 구하는 알고리즘은 다음과 같다
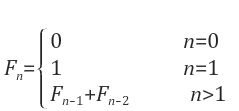
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| int Fibonacci(int n){if(n==0)return 0;if(n==1 || n==2)return 1;return Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2);} |
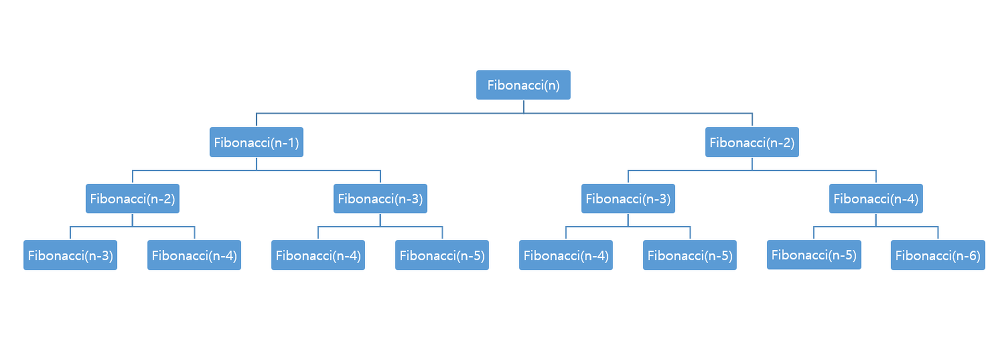 하지만 이 알고리즘은 점점 재귀함수를 호출하는 횟수가 2배씩 늘어서
하지만 이 알고리즘은 점점 재귀함수를 호출하는 횟수가 2배씩 늘어서
시간복잡도가 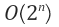 이기 때문에 매우 비효율적이다.
이기 때문에 매우 비효율적이다.
하지만 행렬과 분할정복 기법을 활용하면 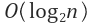 수준으로 알고리즘을 개선할 수 있다.
수준으로 알고리즘을 개선할 수 있다.
2) 동적계획법
//Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming#include<stdio.h>int fib(int n){ /* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */ int f[n+1]; int i; /* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/ f[0] = 0; f[1] = 1; for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) { /* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series and store it */ f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2]; } return f[n];}
3)행렬 연산이용
This another O(n) which relies on the fact that if we n times multiply the matrix M = {{1,1},{1,0}} to itself (in other words calculate power(M, n )), then we get the (n+1)th Fibonacci number as the element at row and column (0, 0) in the resultant matrix.
//Fibonacci Series using Optimized Methodclass fibonacci{ /* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */ static int fib(int n) { int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}}; if (n == 0) return 0; power(F, n-1); return F[0][0]; } static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][]) { int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0]; int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1]; int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0]; int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1]; F[0][0] = x; F[0][1] = y; F[1][0] = z; F[1][1] = w; } /* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */ static void power(int F[][], int n) { if( n == 0 || n == 1) return; int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}}; power(F, n/2); multiply(F, F); if (n%2 != 0) multiply(F, M); } /* Driver program to test above function */ public static void main (String args[]) { int n = 9; System.out.println(fib(n)); }}/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */ |

댓글
댓글 쓰기